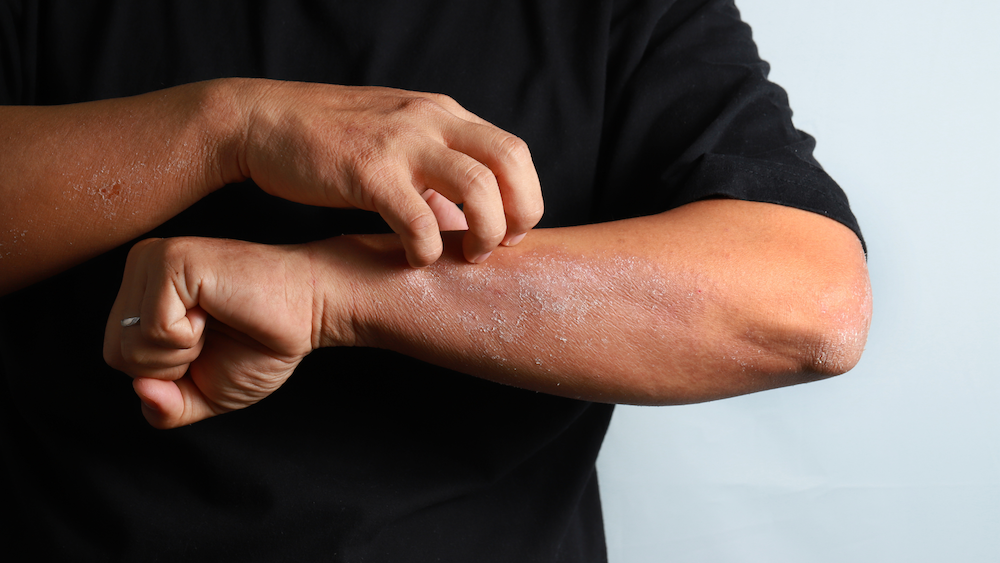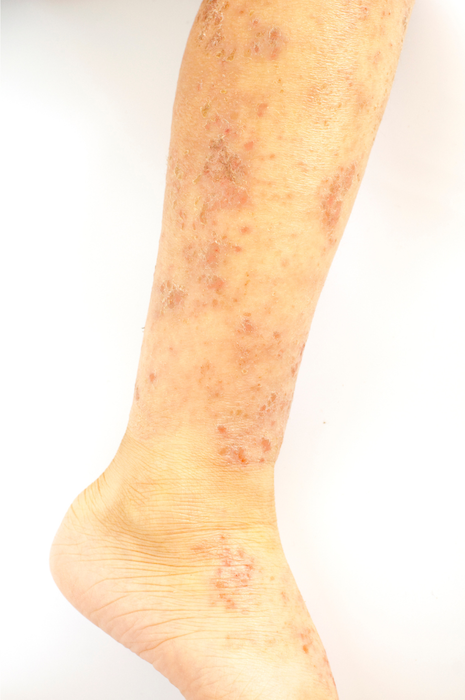
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that affects an estimated 30% of the U.S. population. It is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that can cause the skin to become red, itchy, and irritated.
Eczema is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental elements, and it can be triggered by a variety of factors which we will get into below. The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is thought to be related to an overactive immune system that causes inflammation in the skin.
Eczema can affect different parts of the body, but it is most commonly found on the face, neck, elbows, knees, and ankles.
Visually, eczema can cause the skin to become dry, thickened, and scaly, and it can also cause small, fluid-filled blisters to form. It can also cause the skin to become discolored and can lead to scarring in severe cases.
But what’s going on inside the skin?
How does eczema affect each layer of the skin?
Eczema doesn’t just impact the part of the skin you see, but also each layer of the skin, including the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue.
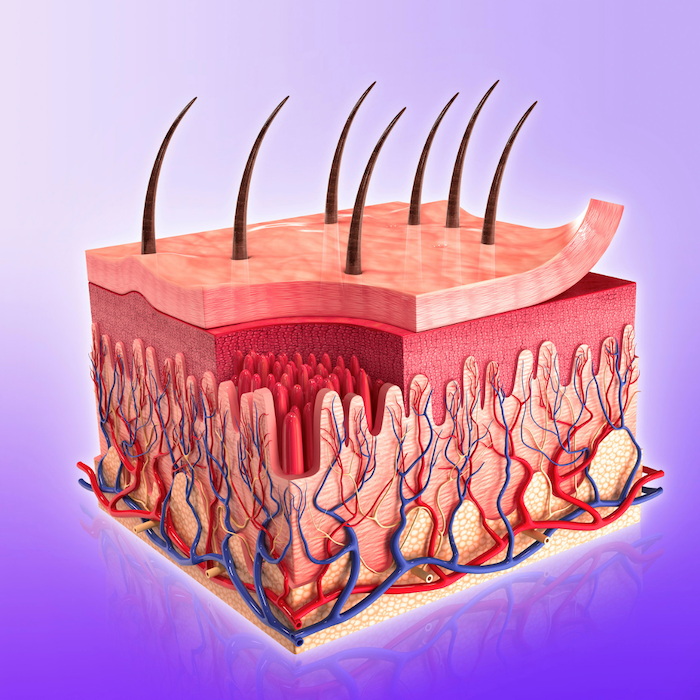
Here’s how:
- Epidermis: The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, and it is the layer that is most visibly affected by eczema. In people with eczema, the epidermis is often dry, scaly, and itchy. This is because eczema disrupts the skin’s barrier function, which makes it harder for the skin to retain moisture and protect against irritants and allergens. When people with eczema itch the affected area, it weakens the skin barrier by breaking away skin cells, making it easier for bacteria to get in, and only worsening the situation.
- Dermis: The dermis is the layer of skin that lies beneath the epidermis, and it contains blood vessels, nerves, and hair follicles. Eczema can cause inflammation in the dermis, which can lead to redness, swelling, and itching. In severe cases, eczema can also cause the dermis to thicken and become leathery in texture.
- Subcutaneous tissue: The subcutaneous tissue is the deepest layer of the skin, and it consists of fat and connective tissue. Eczema can sometimes cause the subcutaneous tissue to become inflamed, which can lead to painful nodules or lumps beneath the skin.
Overall, eczema affects the skin by disrupting its normal function, leading to dryness, inflammation, and itching. This can cause discomfort and can also increase the risk of infections and other complications.
Triggers of eczema breakouts
Unfortunately for those of us with sensitive skin and a proneness to eczema, there are several factors that can trigger a breakout. If you’re susceptible to eczema, below are 7 things that you should be wary of:
- Allergens: Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods can trigger eczema in some people. When a person with eczema comes into contact with an allergen, their immune system can overreact and trigger an inflammatory response in the skin.

- Irritants: Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and other chemicals can also trigger eczema by damaging the skin’s barrier function and causing inflammation. This can make the skin more susceptible to allergens and other irritants, which can further exacerbate eczema symptoms.
- Stress: Stress can trigger eczema by causing the body to release stress hormones, which can affect the immune system and trigger an inflammatory response in the skin. Stress can also lead to changes in skin barrier function, which can make the skin more susceptible to irritants and other triggers.
- Weather: Changes in temperature and humidity can also trigger eczema in some people. Dry, cold weather can cause the skin to become dry and cracked, while hot, humid weather can cause sweating and increased moisture on the skin, which can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
- Infections: Infections such as bacterial or viral infections can trigger eczema by causing inflammation and irritation in the skin. People with eczema are also more susceptible to skin infections due to their compromised skin barrier function.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can trigger eczema in some people. This is because hormones can affect the immune system and the skin’s barrier function, making the skin more susceptible to eczema triggers.
- Foods: Certain foods, such as dairy products, eggs, nuts, and soy, can trigger eczema in some people. This is because these foods contain allergens or other compounds that can trigger an immune response in the skin.
Overall, eczema triggers can vary from person to person, and it’s important for people with eczema to identify their individual triggers and take steps to avoid or minimize them. This can help reduce the frequency and severity of eczema breakouts.
Natural remedies for eczema
If you’re struggling with eczema, all hope is not lost. Not only can you stay mindful of the triggers above, but there are several things you can do at home to help soothe the affected skin.

- Oatmeal baths: Oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe irritated skin. You can add oatmeal to your bathwater or use an oatmeal-based product specifically designed for eczema.
- Coconut oil: Coconut oil is a natural moisturizer that can help hydrate dry skin and reduce inflammation. Apply a thin layer of coconut oil to your skin after bathing to help lock in moisture.
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and soothing properties that can help reduce redness and itching. Apply pure aloe vera gel to your skin to soothe eczema flare-ups.
- Chamomile: Chamomile has anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties that can help soothe irritated skin. You can apply chamomile tea bags to your skin or use a chamomile-based cream or ointment.
- Sunflower seed oil: Sunflower seed oil is a natural emollient that can help moisturize and soothe dry, itchy skin. Apply a few drops of sunflower seed oil to your skin after bathing to help lock in moisture.
- Probiotics: Probiotics can help reduce eczema symptoms by improving gut health and reducing inflammation. You can take probiotic supplements or eat probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut.
- Stress reduction: Stress can trigger eczema flare-ups, so practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing can help reduce eczema symptoms.
While these may offer some help or temporary relief, there’s something you can do that may help in the long term…
CBD for eczema
There is evidence to suggest that using CBD (cannabidiol) may help with eczema symptoms. CBD is a non-psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant that has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and analgesic properties.
Here are some ways in which CBD use may help with eczema:
- Reducing inflammation: CBD has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the skin and alleviate eczema symptoms such as redness, swelling, and itching.
- Moisturizing the skin: CBD has moisturizing properties that can help hydrate dry, itchy skin, which is a common symptom of eczema. CBD-infused topical creams and lotions may help improve skin hydration and reduce skin roughness and dryness.
- Soothing itching and pain: CBD can help reduce the sensation of itching and pain associated with eczema. This is because CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system in the body, which regulates pain and other bodily functions.

- Promoting skin barrier function: CBD can help improve the skin’s barrier function, which is important for people with eczema. A compromised skin barrier can lead to increased moisture loss and susceptibility to irritants and allergens, which can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
If you’re looking for something that can provide relief long term, SomaLeaf’s CBD can help.
Unlike topical CBDs which are never able to help you from the inside out as they can’t penetrate the skin, SomaLeaf’s Micelle Liposomal CBD formula is designed to be fully absorbed and used by your body.
That way, you can actually experience the CBD skin benefits outlined above.
Additionally, many of the triggers and causes of eczema are related to inflammation. Not only can CBD help with this, but turmeric is one of nature’s most powerful anti-inflammatories. And it’s included in our CBD formula.